|
Glossary
EVISA is providing a list of terms used in the area of speciation and fractionation analysis. Since speciation analysis is a field of analytical chemistry that is specified by a pronounced interdisciplinary cooperation between different sciences such as biochemistry, medicine, biology, environmental sciences, nutritional sciences and material sciences its terminology is a complex mixture of terms used in all these.
You may search for a term or browse the glossary alphabetically.
(In case that you cannot find the term you may consult more special glossaries or handbooks about nomenclature. For more details please consult EVISA's Link pages related to terminology,
|
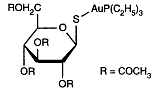 Auranofin is a metallodrug used in treating inflammatory arthritis. Exactly how such gold compounds work is not well understood. In patients with inflammatory arthritis, such as adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, gold salts can decrease the inflammation of the joint lining. Auranofin is a metallodrug used in treating inflammatory arthritis. Exactly how such gold compounds work is not well understood. In patients with inflammatory arthritis, such as adult and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, gold salts can decrease the inflammation of the joint lining.
|
| |
|
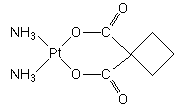 A "second generation" platinum metallodrug effective in cancer chemotherapy that has been approved by the FDA for the treatment of ovarian cancers in 1989. Carboplatin is less toxic than the "first generation" antitumor drug, cisplatin.
IUPAC name: cis-diammine(cyclobutane-1,1-dicarboxylato)platinum(II).
|
| |
|
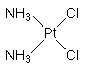 Cisplatin is a "first generation" antitumor drug highly effective in the chemotherapy of many forms of cancer. Thge metallodrug is most commonly used to treat testicular, bladder, lung, gullet (oesophagus), stomach and ovarian cancers. The water-soluble platinum complex, after hydrolysis, reacts with the nucleic acid bases of DNA to produce both intra and interstrand crosslinks. These crosslinks appear to impair replication and transcription of DNA. The cytotoxicity of cisplatin correlates with cellular arrest in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. IUPAC name: cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II).
|
| |
|
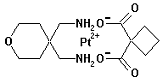 Enloplatin is a platinum metallodrug developed for cancer therapy. Enloplatin is a platinum metallodrug developed for cancer therapy.
Chemical Synonyms (1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato(2-)-O,O')(tetrahydro-4H-pyran- 4,4-dimethanamine-N,N') platinum(II)
CL 287110, CL-287110
CAS Registry No. 111523-41-2
|
| |
|
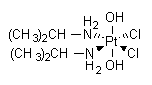 Iproplatin is a second generation metallodrug developed for cancer therapy. Iproplatin binds to and forms DNA crosslinks and platinum-DNA adducts,
resulting in DNA replication failure and cell death. Although less
prone to glutathione inactivation compared to cisplatin, resistance to
this agent has been observed in vitro due to repair of platination
damage by tumor cells.
IUPAC name: cis-dichlorobis(isopropylamine)-trans-dihydroxoplatinum(IV)
|
| |
|
 Lobaplatin (D-19466; 1,2-diammino-methyl-cyclobutaneplatinum(II)-lactate) is a new anticancer agent and a representative of the third-generation platinum compounds. The metallodrug lobaplatin consists of a nearly 50%/50% mixture of two diastereoisomers: (a) the SSS configuration (LP-D1); and (b) the RRS configuration (LP-D2) (see left.) . The compound has shown antitumor activity in human lung, gastric, testicular, and ovarian cancer xenografts, with incomplete cross-resistance to cisplatin in vitro and in vivo. Lobaplatin (D-19466; 1,2-diammino-methyl-cyclobutaneplatinum(II)-lactate) is a new anticancer agent and a representative of the third-generation platinum compounds. The metallodrug lobaplatin consists of a nearly 50%/50% mixture of two diastereoisomers: (a) the SSS configuration (LP-D1); and (b) the RRS configuration (LP-D2) (see left.) . The compound has shown antitumor activity in human lung, gastric, testicular, and ovarian cancer xenografts, with incomplete cross-resistance to cisplatin in vitro and in vivo.
|
| |
|
|
Term used to define a pharmaceutical, having a activity center containing a metal. Platinum (cisplatin, carboplatin) and gold (Auranofin) compounds are well-known in cancer therapy whereas some other gold compounds (aurithiomalate, aurothioglucose) are important antiarthritic drugs. A wide range of Tc compounds (e.g. Tc-labelled antibodies, Tc-mercaptoacetyl glycine complex) are used for diagnostic imaging of renal, cardiac and cerebral functions and of various forms of cancer. Gadolinium (III) polyaminopolycarboxylic crown complexes are widely used as contrast agents in magnetic resonance imaging.
|
| |
|
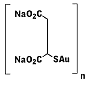 First
generation water-soluble gold(1) thiolate metallodrug used for
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Serious side effects led to the
development of second generation gold drugs such as auranofin. First
generation water-soluble gold(1) thiolate metallodrug used for
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Serious side effects led to the
development of second generation gold drugs such as auranofin.
IUPAC name : auriothiomalate
|
| |
|
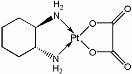 Oxaliplatin (trans-1-diaminocyclohexane oxalatoplatinum) is a platinum-based chemotherapy metallodrug in the same family as cisplatin and carboplatin. Compared to cisplatin the two amine groups are replaced . with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane (DACH) and with an oxalate ligand as a
'leaving group' for improved antitumour activity. A 'leaving group' is an atom or a group of atoms that
is displaced as a stable species taking with it the bonding electrons.
After displacement of the labile oxalate ligand leaving group, active
oxaliplatin derivatives, such as monoaquo and diaquo DACH platinum,
alkylate macromolecules, forming both inter- and intra-strand
platinum-DNA crosslinks, which result in inhibition of DNA replication
and transcription and cell-cycle nonspecific cytotoxicity. The DACH
side chain appears to inhibit alkylating-agent resistance.
CAS number: 61825-94-3
Chemical formula C8H14N2O4Pt
Molecular weight 397.3
|
| |
|
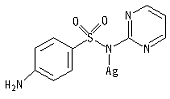 Silver (I) sulfadiazine is a metallodrug used to prevent and treat bacterial or fungus infections of the skin. Silver (I) sulfadiazine is a metallodrug used to prevent and treat bacterial or fungus infections of the skin.
|
| |
|
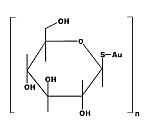 First
generation water-soluble gold(1) thiolate metallodrug used for
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Serious side effects led to the
development of second generation gold drugs such as auranofin. First
generation water-soluble gold(1) thiolate metallodrug used for
treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Serious side effects led to the
development of second generation gold drugs such as auranofin.
IUPAC name : auriothioglucose
|
| |
|
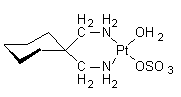 Spiroplatin is a second generation metallodrug and analgue for cisplatin, developed for cancer therapy. Spiroplatin induces DNA cross-links, thereby
inhibiting DNA replication and RNA and protein synthesis. Similar to
other platinum compounds, this agent has been shown to be mutagenic and
carcinogenic.
IUPAC name: aqua-1,1-bis(aminomethyl)-cyclohexanesulfatoplatinum(II)
|
| |
|